Bounded density estimator using the reflection method.
Supports automatic partial function application with waived arguments.
Usage
density_bounded(
x,
weights = NULL,
n = 501,
bandwidth = "dpi",
adjust = 1,
kernel = "gaussian",
trim = TRUE,
bounds = c(NA, NA),
bounder = "cdf",
adapt = 1,
na.rm = FALSE,
...,
range_only = FALSE
)Arguments
- x
<numeric> Sample to compute a density estimate for.
- weights
- n
<scalar numeric> The number of grid points to evaluate the density estimator at.
- bandwidth
<scalar numeric | function | string> Bandwidth of the density estimator. One of:
a numeric: the bandwidth, as the standard deviation of the kernel
a function: a function taking
x(the sample) and returning the bandwidtha string: the suffix of the name of a function starting with
"bandwidth_"that will be used to determine the bandwidth. See bandwidth for a list.
- adjust
<scalar numeric> Value to multiply the bandwidth of the density estimator by. Default
1.- kernel
<string> The smoothing kernel to be used. This must partially match one of
"gaussian","rectangular","triangular","epanechnikov","biweight","cosine", or"optcosine". Seestats::density().- trim
<scalar logical> Should the density estimate be trimmed to the range of the data? Default
TRUE.- bounds
<length-2 numeric> Min and max bounds. If a bound is
NA, then that bound is estimated from the data using the method specified bybounder.- bounder
<function | string> Method to use to find missing (
NA)bounds. A function that takes a numeric vector of values and returns a length-2 vector of the estimated lower and upper bound of the distribution. Can also be a string giving the suffix of the name of such a function that starts with"bounder_". Useful values include:"cdf": Use the CDF of the the minimum and maximum order statistics of the sample to estimate the bounds. Seebounder_cdf()."cooke": Use the method from Cooke (1979); i.e. method 2.3 from Loh (1984). Seebounder_cooke()."range": Use the range ofx(i.e theminormax). Seebounder_range().
- adapt
<positive integer> (very experimental) The name and interpretation of this argument are subject to change without notice. If
adapt > 1, uses an adaptive approach to calculate the density. First, uses the adaptive bandwidth algorithm of Abramson (1982) to determine local (pointwise) bandwidths, then groups these bandwidths intoadaptgroups, then calculates and sums the densities from each group. You can set this to a very large number (e.g.Inf) for a fully adaptive approach, but this will be very slow; typically something around 100 yields nearly identical results.- na.rm
<scalar logical> Should missing (
NA) values inxbe removed?- ...
Additional arguments (ignored).
- range_only
<scalar logical> If
TRUE, the range of the output of this density estimator is computed and is returned in the$xelement of the result, andc(NA, NA)is returned in$y. This gives a faster way to determine the range of the output thandensity_XXX(n = 2).
Value
An object of class "density", mimicking the output format of
stats::density(), with the following components:
x: The grid of points at which the density was estimated.y: The estimated density values.bw: The bandwidth.n: The sample size of thexinput argument.call: The call used to produce the result, as a quoted expression.data.name: The deparsed name of thexinput argument.has.na: AlwaysFALSE(for compatibility).cdf: Values of the (possibly weighted) empirical cumulative distribution function atx. Seeweighted_ecdf().
This allows existing methods for density objects, like print() and plot(), to work if desired.
This output format (and in particular, the x and y components) is also
the format expected by the density argument of the stat_slabinterval()
and the smooth_ family of functions.
References
Cooke, P. (1979). Statistical inference for bounds of random variables. Biometrika 66(2), 367–374. doi:10.1093/biomet/66.2.367 .
Loh, W. Y. (1984). Estimating an endpoint of a distribution with resampling methods. The Annals of Statistics 12(4), 1543–1550. doi:10.1214/aos/1176346811
See also
Other density estimators:
density_histogram(),
density_unbounded()
Examples
library(distributional)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
# For compatibility with existing code, the return type of density_bounded()
# is the same as stats::density(), ...
set.seed(123)
x = rbeta(5000, 1, 3)
d = density_bounded(x)
d
#>
#> Call:
#> density_bounded(x = x)
#>
#> Data: x (5000 obs.); Bandwidth 'bw' = 0.01647
#>
#> x y
#> Min. :3.377e-05 Min. :0.01634
#> 1st Qu.:2.368e-01 1st Qu.:0.26379
#> Median :4.736e-01 Median :0.91029
#> Mean :4.736e-01 Mean :1.05591
#> 3rd Qu.:7.104e-01 3rd Qu.:1.66224
#> Max. :9.471e-01 Max. :2.90384
# ... thus, while designed for use with the `density` argument of
# stat_slabinterval(), output from density_bounded() can also be used with
# base::plot():
plot(d)
 # here we'll use the same data as above, but pick either density_bounded()
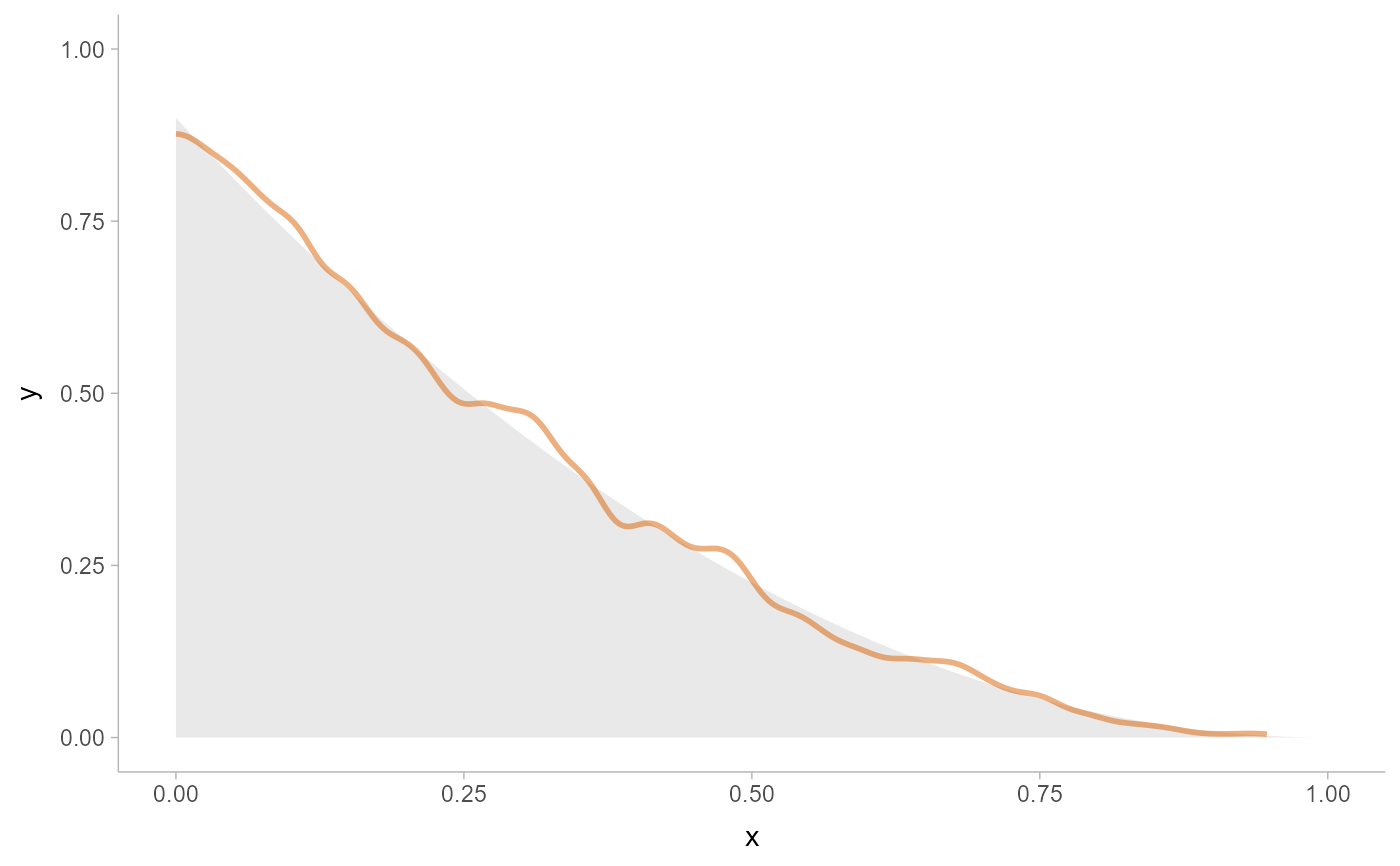
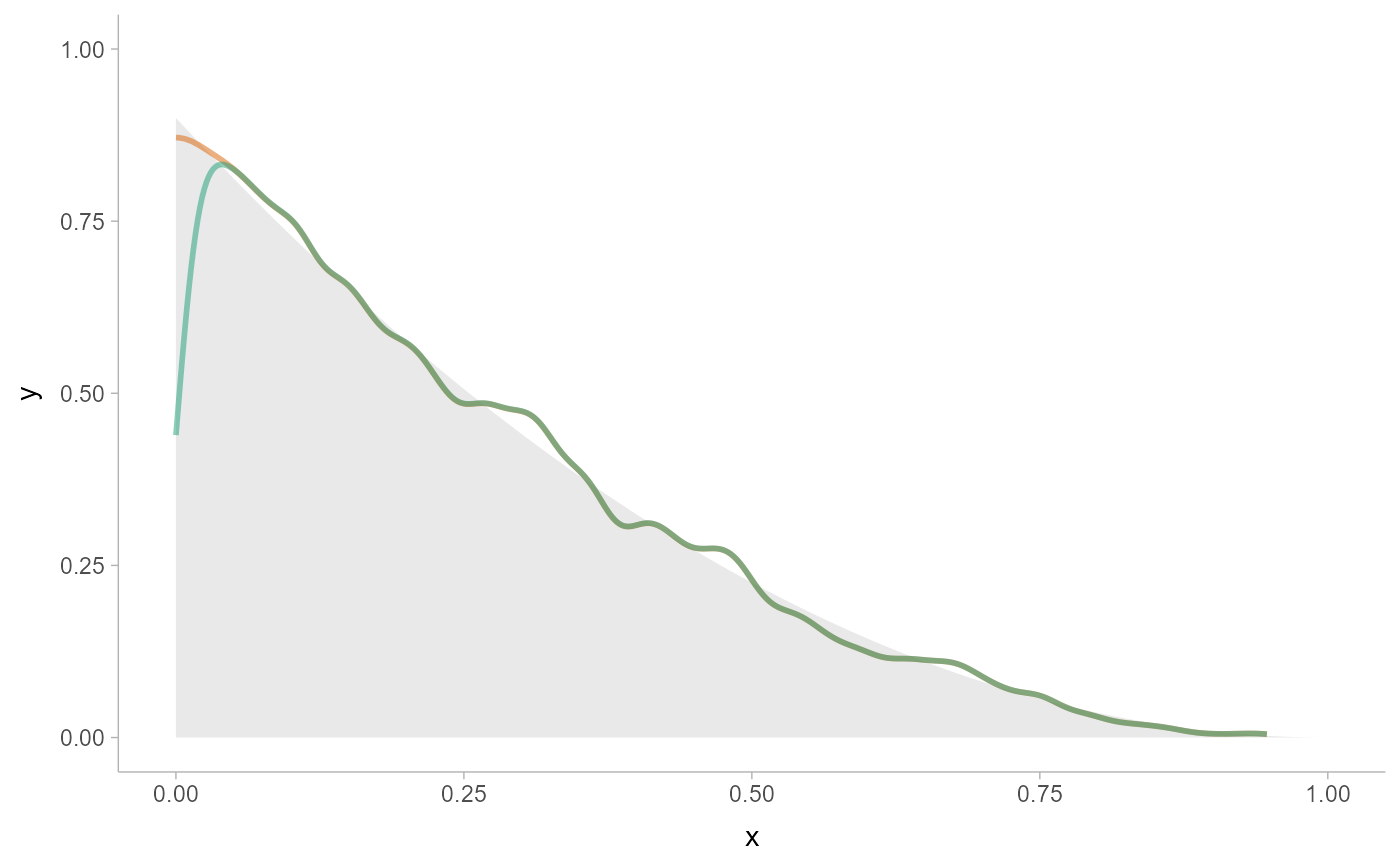
# or density_unbounded() (which is equivalent to stats::density()). Notice
# how the bounded density (green) is biased near the boundary of the support,
# while the unbounded density is not.
data.frame(x) %>%
ggplot() +
stat_slab(
aes(xdist = dist), data = data.frame(dist = dist_beta(1, 3)),
alpha = 0.25
) +
stat_slab(aes(x), density = "bounded", fill = NA, color = "#d95f02", alpha = 0.5) +
stat_slab(aes(x), density = "unbounded", fill = NA, color = "#1b9e77", alpha = 0.5) +
scale_thickness_shared() +
theme_ggdist()
# here we'll use the same data as above, but pick either density_bounded()
# or density_unbounded() (which is equivalent to stats::density()). Notice
# how the bounded density (green) is biased near the boundary of the support,
# while the unbounded density is not.
data.frame(x) %>%
ggplot() +
stat_slab(
aes(xdist = dist), data = data.frame(dist = dist_beta(1, 3)),
alpha = 0.25
) +
stat_slab(aes(x), density = "bounded", fill = NA, color = "#d95f02", alpha = 0.5) +
stat_slab(aes(x), density = "unbounded", fill = NA, color = "#1b9e77", alpha = 0.5) +
scale_thickness_shared() +
theme_ggdist()
 # We can also supply arguments to the density estimators by using their
# full function names instead of the string suffix; e.g. we can supply
# the exact bounds of c(0,1) rather than using the bounds of the data.
data.frame(x) %>%
ggplot() +
stat_slab(
aes(xdist = dist), data = data.frame(dist = dist_beta(1, 3)),
alpha = 0.25
) +
stat_slab(
aes(x), fill = NA, color = "#d95f02", alpha = 0.5,
density = density_bounded(bounds = c(0,1))
) +
scale_thickness_shared() +
theme_ggdist()
# We can also supply arguments to the density estimators by using their
# full function names instead of the string suffix; e.g. we can supply
# the exact bounds of c(0,1) rather than using the bounds of the data.
data.frame(x) %>%
ggplot() +
stat_slab(
aes(xdist = dist), data = data.frame(dist = dist_beta(1, 3)),
alpha = 0.25
) +
stat_slab(
aes(x), fill = NA, color = "#d95f02", alpha = 0.5,
density = density_bounded(bounds = c(0,1))
) +
scale_thickness_shared() +
theme_ggdist()