Shortcut version of geom_slabinterval() for creating point + multiple-interval plots.
Roughly equivalent to:
geom_slabinterval(
aes(
datatype = "interval",
side = "both"
),
show_slab = FALSE,
show.legend = c(size = FALSE)
)Usage
geom_pointinterval(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "identity",
position = "identity",
...,
orientation = NA,
interval_size_domain = c(1, 6),
interval_size_range = c(0.6, 1.4),
fatten_point = 1.8,
arrow = NULL,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = c(size = FALSE),
inherit.aes = TRUE,
check.aes = TRUE,
check.param = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
aes(). If specified andinherit.aes = TRUE(the default), it is combined with the default mapping at the top level of the plot. You must supplymappingif there is no plot mapping.- data
The data to be displayed in this layer. There are three options:
If
NULL, the default, the data is inherited from the plot data as specified in the call toggplot().A
data.frame, or other object, will override the plot data. All objects will be fortified to produce a data frame. Seefortify()for which variables will be created.A
functionwill be called with a single argument, the plot data. The return value must be adata.frame, and will be used as the layer data. Afunctioncan be created from aformula(e.g.~ head(.x, 10)).- stat
The statistical transformation to use on the data for this layer. When using a
geom_*()function to construct a layer, thestatargument can be used to override the default coupling between geoms and stats. Thestatargument accepts the following:A
Statggproto subclass, for exampleStatCount.A string naming the stat. To give the stat as a string, strip the function name of the
stat_prefix. For example, to usestat_count(), give the stat as"count".For more information and other ways to specify the stat, see the layer stat documentation.
- position
<Position | string> Position adjustment, either as a string, or the result of a call to a position adjustment function. Setting this equal to
"dodge"(position_dodge()) or"dodgejust"(position_dodgejust()) can be useful if you have overlapping geometries.- ...
Other arguments passed to
layer(). These are often aesthetics, used to set an aesthetic to a fixed value, likecolour = "red"orlinewidth = 3(see Aesthetics, below). They may also be parameters to the paired geom/stat.- orientation
<string> Whether this geom is drawn horizontally or vertically. One of:
NA(default): automatically detect the orientation based on how the aesthetics are assigned. Automatic detection works most of the time."horizontal"(or"y"): draw horizontally, using theyaesthetic to identify different groups. For each group, uses thex,xmin,xmax, andthicknessaesthetics to draw points, intervals, and slabs."vertical"(or"x"): draw vertically, using thexaesthetic to identify different groups. For each group, uses they,ymin,ymax, andthicknessaesthetics to draw points, intervals, and slabs.
For compatibility with the base ggplot naming scheme for
orientation,"x"can be used as an alias for"vertical"and"y"as an alias for"horizontal"(ggdist had anorientationparameter before base ggplot did, hence the discrepancy).- interval_size_domain
<length-2 numeric> Minimum and maximum of the values of the
sizeandlinewidthaesthetics that will be translated into actual sizes for intervals drawn according tointerval_size_range(see the documentation for that argument.)- interval_size_range
<length-2 numeric> This geom scales the raw size aesthetic values when drawing interval and point sizes, as they tend to be too thick when using the default settings of
scale_size_continuous(), which give sizes with a range ofc(1, 6). Theinterval_size_domainvalue indicates the input domain of raw size values (typically this should be equal to the value of therangeargument of thescale_size_continuous()function), andinterval_size_rangeindicates the desired output range of the size values (the min and max of the actual sizes used to draw intervals). Most of the time it is not recommended to change the value of this argument, as it may result in strange scaling of legends; this argument is a holdover from earlier versions that did not have size aesthetics targeting the point and interval separately. If you want to adjust the size of the interval or points separately, you can also use thelinewidthorpoint_sizeaesthetics; see sub-geometry-scales.- fatten_point
<scalar numeric> A multiplicative factor used to adjust the size of the point relative to the size of the thickest interval line. If you wish to specify point sizes directly, you can also use the
point_sizeaesthetic andscale_point_size_continuous()orscale_point_size_discrete(); sizes specified with that aesthetic will not be adjusted usingfatten_point.- arrow
<arrow | NULL> Type of arrow heads to use on the interval, or
NULLfor no arrows.- na.rm
<scalar logical> If
FALSE, the default, missing values are removed with a warning. IfTRUE, missing values are silently removed.- show.legend
<logical> Should this layer be included in the legends? Default is
c(size = FALSE), unlike most geoms, to match its common use cases.FALSEhides all legends,TRUEshows all legends, andNAshows only those that are mapped (the default for most geoms). It can also be a named logical vector to finely select the aesthetics to display.- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics, rather than combining with them. This is most useful for helper functions that define both data and aesthetics and shouldn't inherit behaviour from the default plot specification, e.g.annotation_borders().- check.aes, check.param
If
TRUE, the default, will check that supplied parameters and aesthetics are understood by thegeomorstat. UseFALSEto suppress the checks.
Value
A ggplot2::Geom representing a point + multiple-interval geometry which can
be added to a ggplot() object.
Details
This geom wraps geom_slabinterval() with defaults designed to produce
point + multiple-interval plots. Default aesthetic mappings are applied if the .width column
is present in the input data (e.g., as generated by the point_interval() family of functions),
making this geom often more convenient than vanilla ggplot2 geometries when used with
functions like median_qi(), mean_qi(), mode_hdi(), etc.
Specifically, if .width is present in the input, geom_pointinterval() acts
as if its default aesthetics are aes(size = -.width)
Aesthetics
The slab+interval stats and geoms have a wide variety of aesthetics that control
the appearance of their three sub-geometries: the slab, the point, and
the interval.
Positional aesthetics
x: x position of the geometryy: y position of the geometry
Interval-specific aesthetics
xmin: Left end of the interval sub-geometry (iforientation = "horizontal").xmax: Right end of the interval sub-geometry (iforientation = "horizontal").ymin: Lower end of the interval sub-geometry (iforientation = "vertical").ymax: Upper end of the interval sub-geometry (iforientation = "vertical").
Point-specific aesthetics
shape: Shape type used to draw the point sub-geometry.
Color aesthetics
colour: (orcolor) The color of the interval and point sub-geometries. Use theslab_color,interval_color, orpoint_coloraesthetics (below) to set sub-geometry colors separately.fill: The fill color of the slab and point sub-geometries. Use theslab_fillorpoint_fillaesthetics (below) to set sub-geometry colors separately.alpha: The opacity of the slab, interval, and point sub-geometries. Use theslab_alpha,interval_alpha, orpoint_alphaaesthetics (below) to set sub-geometry colors separately.colour_ramp: (orcolor_ramp) A secondary scale that modifies thecolorscale to "ramp" to another color. Seescale_colour_ramp()for examples.fill_ramp: A secondary scale that modifies thefillscale to "ramp" to another color. Seescale_fill_ramp()for examples.
Line aesthetics
linewidth: Width of the line used to draw the interval (except withgeom_slab(): then it is the width of the slab). With composite geometries including an interval and slab, useslab_linewidthto set the line width of the slab (see below). For interval, rawlinewidthvalues are transformed according to theinterval_size_domainandinterval_size_rangeparameters of thegeom(see above).size: Determines the size of the point. Iflinewidthis not provided,sizewill also determines the width of the line used to draw the interval (this allows line width and point size to be modified together by setting onlysizeand notlinewidth). Rawsizevalues are transformed according to theinterval_size_domain,interval_size_range, andfatten_pointparameters of thegeom(see above). Use thepoint_sizeaesthetic (below) to set sub-geometry size directly without applying the effects ofinterval_size_domain,interval_size_range, andfatten_point.stroke: Width of the outline around the point sub-geometry.linetype: Type of line (e.g.,"solid","dashed", etc) used to draw the interval and the outline of the slab (if it is visible). Use theslab_linetypeorinterval_linetypeaesthetics (below) to set sub-geometry line types separately.
Interval-specific color and line override aesthetics
interval_colour: (orinterval_color) Override forcolour/color: the color of the interval.interval_alpha: Override foralpha: the opacity of the interval.interval_linetype: Override forlinetype: the line type of the interval.
Point-specific color and line override aesthetics
point_fill: Override forfill: the fill color of the point.point_colour: (orpoint_color) Override forcolour/color: the outline color of the point.point_alpha: Override foralpha: the opacity of the point.point_size: Override forsize: the size of the point.
Deprecated aesthetics
interval_size: Useinterval_linewidth.
Other aesthetics (these work as in standard geoms)
widthheightgroup
See examples of some of these aesthetics in action in vignette("slabinterval").
Learn more about the sub-geom override aesthetics (like interval_color) in the
scales documentation. Learn more about basic ggplot aesthetics in
vignette("ggplot2-specs").
See also
See stat_pointinterval() for the stat version, intended for
use on sample data or analytical distributions.
See geom_slabinterval() for the geometry this shortcut is based on.
Other slabinterval geoms:
geom_interval(),
geom_slab(),
geom_spike()
Examples
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
data(RankCorr_u_tau, package = "ggdist")
# orientation is detected automatically based on
# use of xmin/xmax or ymin/ymax
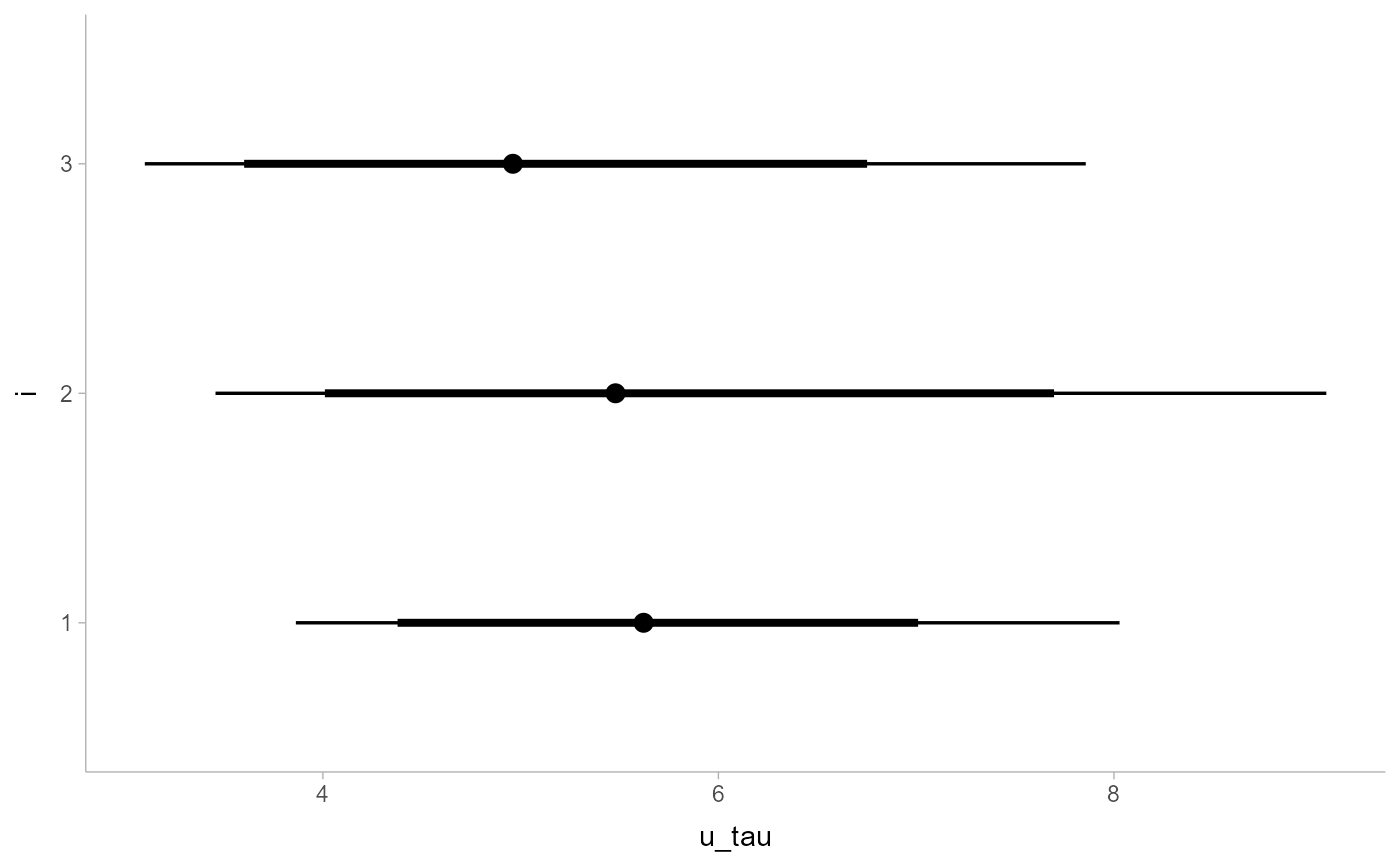
RankCorr_u_tau %>%
group_by(i) %>%
median_qi(.width = c(.8, .95)) %>%
ggplot(aes(y = i, x = u_tau, xmin = .lower, xmax = .upper)) +
geom_pointinterval()
 RankCorr_u_tau %>%
group_by(i) %>%
median_qi(.width = c(.8, .95)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = i, y = u_tau, ymin = .lower, ymax = .upper)) +
geom_pointinterval()
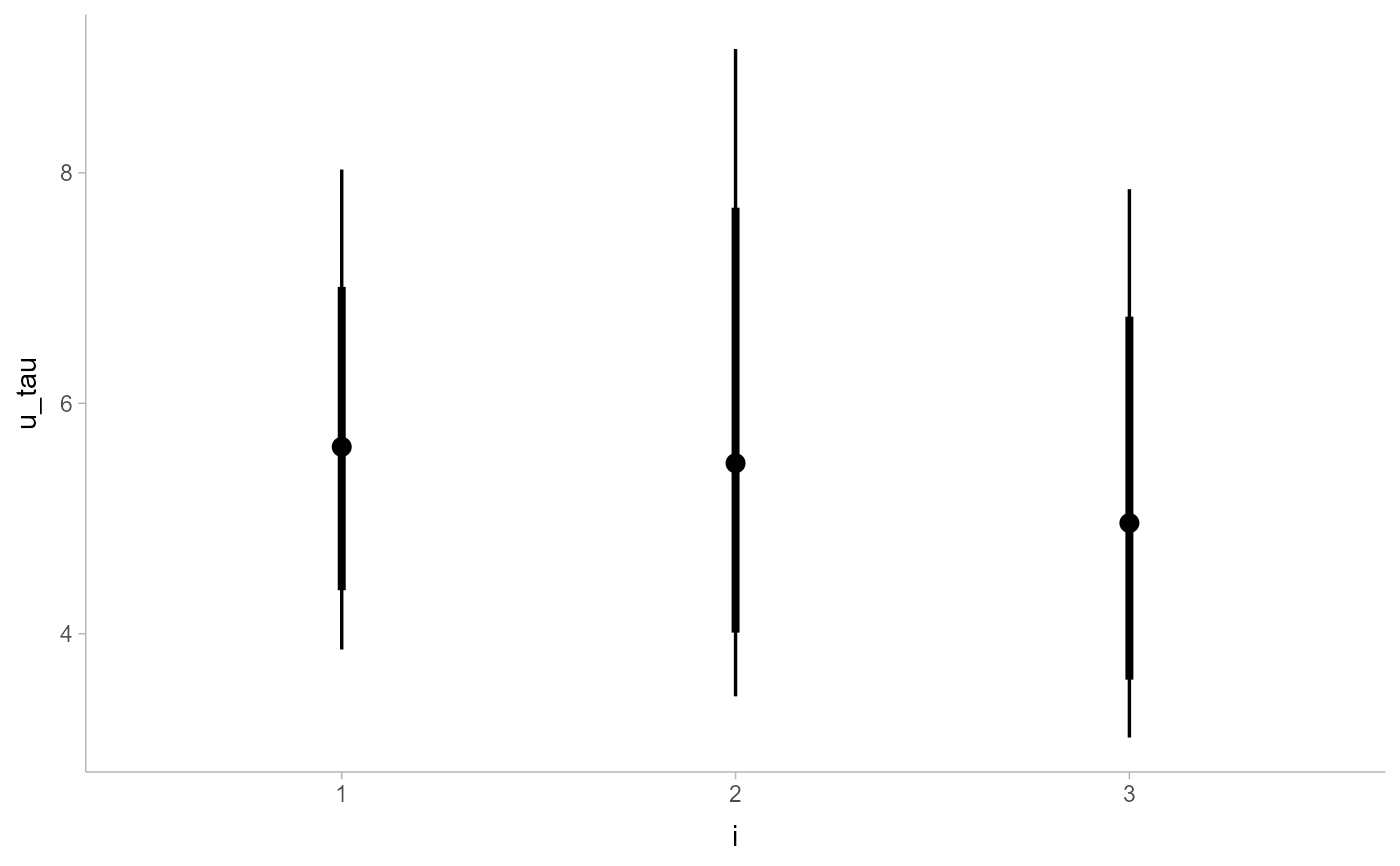
RankCorr_u_tau %>%
group_by(i) %>%
median_qi(.width = c(.8, .95)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = i, y = u_tau, ymin = .lower, ymax = .upper)) +
geom_pointinterval()