Generates a data frame of bins representing the kernel density (or
histogram) of a vector, suitable for use in generating predictive
distributions for visualization. These functions were originally
designed for use with the now-deprecated predict_curve(), and
may be deprecated in the future.
density_bins(x, n = 101, ...)
histogram_bins(x, n = 30, breaks = n, ...)Arguments
Value
A data frame representing bins and their densities with the following columns:
- mid
Bin midpoint
- lower
Lower endpoint of each bin
- upper
Upper endpoint of each bin
- density
Density estimate of the bin
Details
These functions are simple wrappers to density() and
hist() that compute density estimates and return their results
in a consistent format: a data frame of bins suitable for use with
the now-deprecated predict_curve().
density_bins computes a kernel density estimate using
density().
histogram_bins computes a density histogram using hist().
See also
See add_predicted_draws() and stat_lineribbon() for a better approach. These
functions may be deprecated in the future.
Examples
# \dontrun{
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
library(brms)
library(modelr)
theme_set(theme_light())
m_mpg = brm(mpg ~ hp * cyl, data = mtcars)
#> Compiling Stan program...
#> Start sampling
#>
#> SAMPLING FOR MODEL 'anon_model' NOW (CHAIN 1).
#> Chain 1:
#> Chain 1: Gradient evaluation took 5.8e-05 seconds
#> Chain 1: 1000 transitions using 10 leapfrog steps per transition would take 0.58 seconds.
#> Chain 1: Adjust your expectations accordingly!
#> Chain 1:
#> Chain 1:
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 1 / 2000 [ 0%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 200 / 2000 [ 10%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 400 / 2000 [ 20%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 600 / 2000 [ 30%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 800 / 2000 [ 40%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 1000 / 2000 [ 50%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 1001 / 2000 [ 50%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 1200 / 2000 [ 60%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 1400 / 2000 [ 70%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 1600 / 2000 [ 80%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 1800 / 2000 [ 90%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 1: Iteration: 2000 / 2000 [100%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 1:
#> Chain 1: Elapsed Time: 0.34 seconds (Warm-up)
#> Chain 1: 0.175 seconds (Sampling)
#> Chain 1: 0.515 seconds (Total)
#> Chain 1:
#>
#> SAMPLING FOR MODEL 'anon_model' NOW (CHAIN 2).
#> Chain 2:
#> Chain 2: Gradient evaluation took 6e-06 seconds
#> Chain 2: 1000 transitions using 10 leapfrog steps per transition would take 0.06 seconds.
#> Chain 2: Adjust your expectations accordingly!
#> Chain 2:
#> Chain 2:
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 1 / 2000 [ 0%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 200 / 2000 [ 10%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 400 / 2000 [ 20%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 600 / 2000 [ 30%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 800 / 2000 [ 40%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 1000 / 2000 [ 50%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 1001 / 2000 [ 50%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 1200 / 2000 [ 60%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 1400 / 2000 [ 70%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 1600 / 2000 [ 80%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 1800 / 2000 [ 90%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 2: Iteration: 2000 / 2000 [100%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 2:
#> Chain 2: Elapsed Time: 0.318 seconds (Warm-up)
#> Chain 2: 0.132 seconds (Sampling)
#> Chain 2: 0.45 seconds (Total)
#> Chain 2:
#>
#> SAMPLING FOR MODEL 'anon_model' NOW (CHAIN 3).
#> Chain 3:
#> Chain 3: Gradient evaluation took 7e-06 seconds
#> Chain 3: 1000 transitions using 10 leapfrog steps per transition would take 0.07 seconds.
#> Chain 3: Adjust your expectations accordingly!
#> Chain 3:
#> Chain 3:
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 1 / 2000 [ 0%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 200 / 2000 [ 10%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 400 / 2000 [ 20%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 600 / 2000 [ 30%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 800 / 2000 [ 40%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 1000 / 2000 [ 50%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 1001 / 2000 [ 50%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 1200 / 2000 [ 60%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 1400 / 2000 [ 70%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 1600 / 2000 [ 80%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 1800 / 2000 [ 90%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 3: Iteration: 2000 / 2000 [100%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 3:
#> Chain 3: Elapsed Time: 0.318 seconds (Warm-up)
#> Chain 3: 0.194 seconds (Sampling)
#> Chain 3: 0.512 seconds (Total)
#> Chain 3:
#>
#> SAMPLING FOR MODEL 'anon_model' NOW (CHAIN 4).
#> Chain 4:
#> Chain 4: Gradient evaluation took 6e-06 seconds
#> Chain 4: 1000 transitions using 10 leapfrog steps per transition would take 0.06 seconds.
#> Chain 4: Adjust your expectations accordingly!
#> Chain 4:
#> Chain 4:
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 1 / 2000 [ 0%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 200 / 2000 [ 10%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 400 / 2000 [ 20%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 600 / 2000 [ 30%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 800 / 2000 [ 40%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 1000 / 2000 [ 50%] (Warmup)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 1001 / 2000 [ 50%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 1200 / 2000 [ 60%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 1400 / 2000 [ 70%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 1600 / 2000 [ 80%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 1800 / 2000 [ 90%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 4: Iteration: 2000 / 2000 [100%] (Sampling)
#> Chain 4:
#> Chain 4: Elapsed Time: 0.257 seconds (Warm-up)
#> Chain 4: 0.139 seconds (Sampling)
#> Chain 4: 0.396 seconds (Total)
#> Chain 4:
step = 1
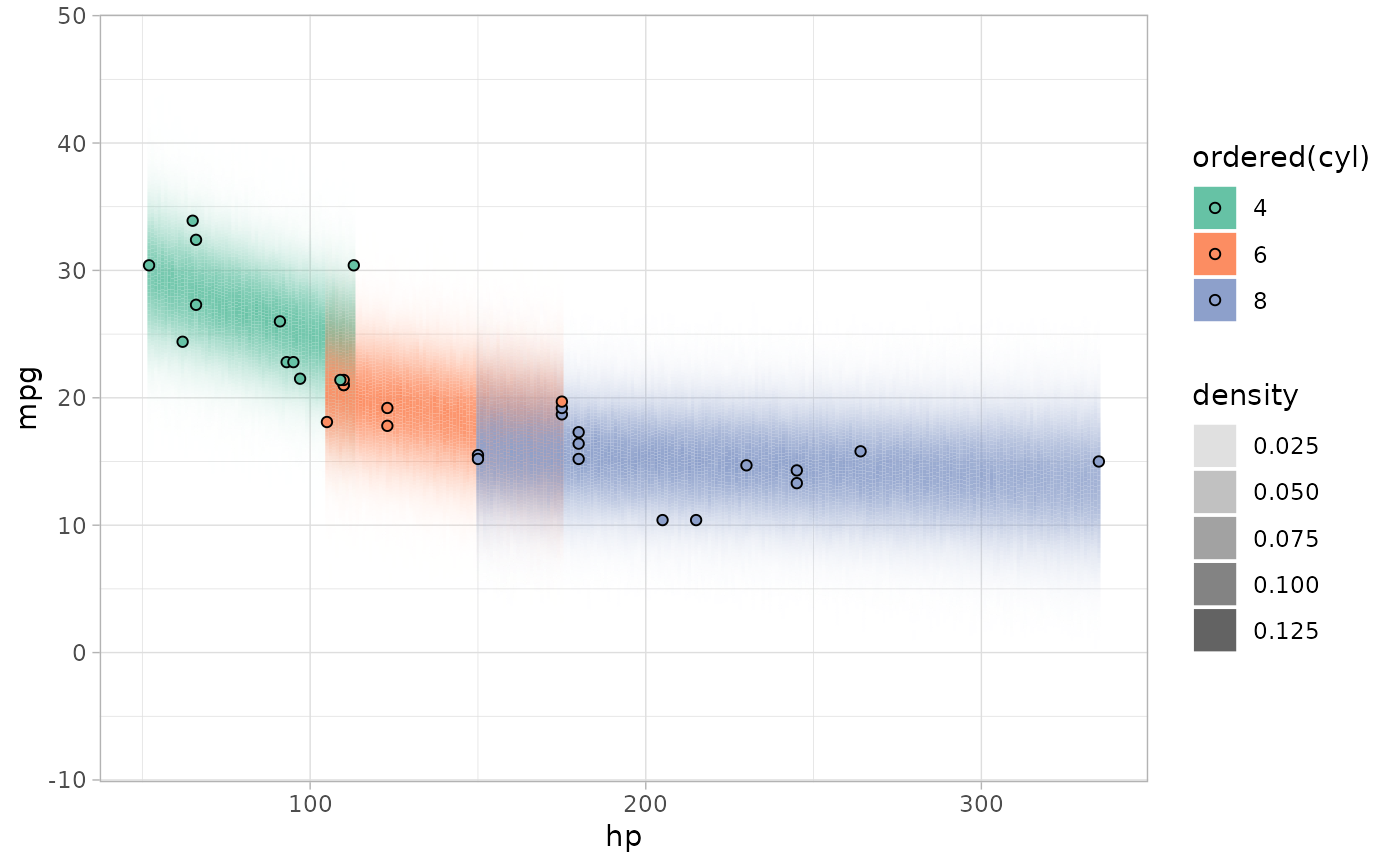
mtcars %>%
group_by(cyl) %>%
data_grid(hp = seq_range(hp, by = step)) %>%
add_predicted_draws(m_mpg) %>%
summarise(density_bins(.prediction), .groups = "drop") %>%
ggplot() +
geom_rect(aes(
xmin = hp - step/2, ymin = lower, ymax = upper, xmax = hp + step/2,
fill = ordered(cyl), alpha = density
)) +
geom_point(aes(x = hp, y = mpg, fill = ordered(cyl)), shape = 21, data = mtcars) +
scale_alpha_continuous(range = c(0, 1)) +
scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Set2")
#> Warning: Returning more (or less) than 1 row per `summarise()` group was deprecated in
#> dplyr 1.1.0.
#> ℹ Please use `reframe()` instead.
#> ℹ When switching from `summarise()` to `reframe()`, remember that `reframe()`
#> always returns an ungrouped data frame and adjust accordingly.
 # }
# }